WHAT IS A CRM SYSTEM?
The guide for beginners
With customer relationship management (CRM for short), you put your customer’s needs at the center of all business processes. Basic goals are customer acquisition and customer retention.
To do this, you not only formulate an individual strategy, but also let a suitable CRM system support you in designing customer-friendly processes throughout the company.
The following information provides practical tips and makes it easier to enter the world of customer relationship management.

For those in a hurry: Save the content of this page as a PDF, read it later and share it with others!

Table of Content
What is a CRM, a CRM software, a CRM system?
A clarification of terms is necessary
Different perspectives on customer relationship management
There is not THE ONE definition, because Customer Relationship Management is not an isolated instrument, but flows into the business processes as part of the corporate philosophy. Therefore, the respective structure of the company determines the individual CRM definition. Learn more about goals, forms & strategies in our blog article CRM Definition.
Click image to enlarge.
Five important CRM terms
1. CRM definition: short, concise, understandable
Customer relationship management is the orientation of a company towards its customers. The basic goals are customer acquisition and customer loyalty. Therefore, Customer Relationship Management deals with designing business processes around existing and potential customers. By capturing all relevant data with CRM software, marketing can be precisely targeted to the needs of customers and is consequently called relationship marketing. This management concept enables the increase of the company’s success.
So when we talk about CRM, we usually mean one of these three points:
- CRM as software: Often also referred to as CRM system or CRM solution. It provides the technological foundation for capturing, analyzing, and presenting business interactions with customers or other relationships.
- CRM as a strategy: This refers to the conscious orientation of corporate processes toward the customer or an optimal customer experience.
- CRM as a process: This refers to the extensive processes for customer orientation. These include not only the technological, but also strategic, systematic approaches of a company.
2. CRM software
Software supports the optimization of customer relationship management. It records all relevant customer data and transactions in a structured manner and thus relieves the burden on the various divisions that are related to customers. The software increases the efficiency of all areas and relationships. For example, CRM software can be used to create offers for individual customers or customer groups individually. Or the company increases customer loyalty by tailor-made service. Further and more detailed information can be found here:
3. introduction of a CRM system
CRM implementation deals on the one hand with the implementation of the customer software in the company and on the other hand with the design of the customer management processes. The typical project for this is divided into the seven phases: Requirements analysis, technical implementation, pilot operation, user training, reorganization, rollout and acceptance.
4. the most important approaches
- Analytical CRM:
Evaluate data from operations based on KPIs to evaluate product requirements. - Operational CRM:
The supporting function of the CRM system for the departments to initiate contacts and maintain customer relationships. - Collaborative CRM:
Deals with cooperation within the company and with external partners. - Communicative CRM:
Manages all communication channels with alignment to the customer. - Social CRM:
Extension of classic customer relationship management through dialog with users of social media channels, i.e. social networks such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, XING, etc. (social media integration)
5. relationship management with all stakeholders of a company = xRM
xRM (any-relationship management) is based on customer relationship management and, as an advanced form, deals with the design of relationships with all contacts of a company (customers, partners, suppliers, employees, machines). This also includes all linked processes such as projects, contracts, logs, inventory, etc.
More information about xRM
Excursus: What does CRM have to do with Customer Centricity?
Customer Centricity (or customer centricity) is a core element of CRM and makes up a large part of the CRM strategy. It is a question of what the customer wants and what he might want in the future, in order to develop products and services according to these wishes. This puts the customer at the center of the company and its actions.
CRM is the basis for centering: not only because all customer data is stored centrally here, but also because corresponding measures can be planned with it, tasks can be defined and partially executed automatically. In CRM, data on all customer touch points with the company and its offerings are recorded and evaluated. This provides an overview of the customer journey, from the very first contact to the purchase of a product or service. The more complete the documentation, the more precisely tailored or personalized content can be played out for the next contacts after the first contacts, so that the customer has many positive experiences with the company, products and services (= called customer experience management ).
For whom is a CRM system suitable?
Areas & industries for use
Are you wondering if your employees even need a tool? And if so, are everyone really? Find out in our blog article Who needs CRM? which areas of the company benefit from this type of software.
Tool for
Teams
- Procurement
- Event management
- Finance & Accounting
- Marketing
- Employee development
- Public administration
- Recruiting
- Service & IT
- Sales
- Central management
Tool for
Industries
Tool for
Company sizes
- Corporations & large companies
- Medium-sized companies
- Small businesses & start ups
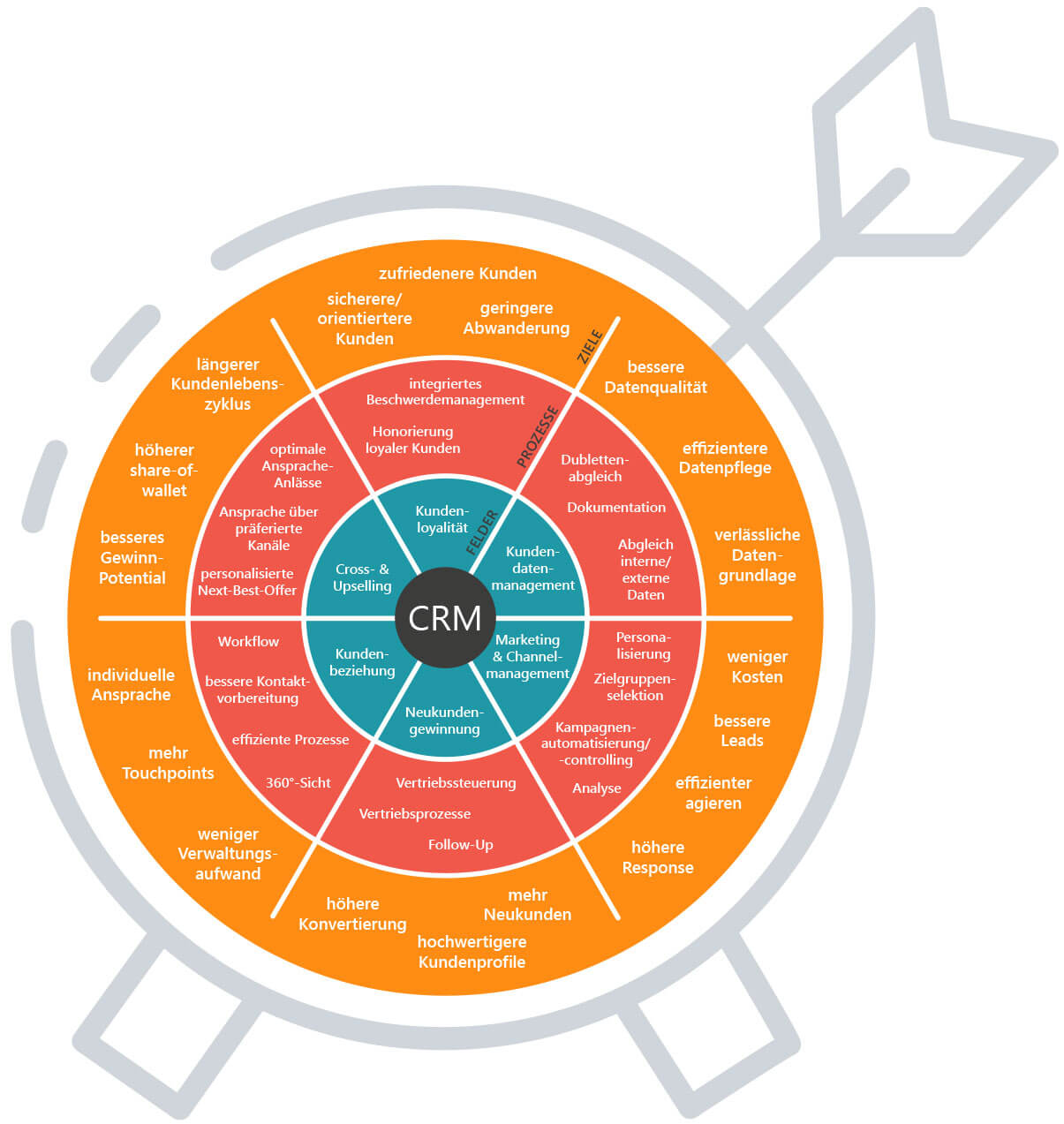
Advantages and goals of a CRM system
Why use a CRM in your company? What goals does that bring you closer to?
A good system holds numerous advantages for you and your employees. You promote transparent, team-oriented work, increase the efficiency of your various departments and provide key figures for analyses and conclusions. These are all small goals on the way to building stronger loyalty with existing customers and generating new ones. At the end of this journey, the goal is to use the customer loyalty system to create all-around positive customer experiences (=. Customer Experience).
Read more about the benefits of a CRM system in our blog article.
What do you use a CRM system for specifically?
In practice, you use a CRM system primarily with the aim of being able to track and optimally design the interactions with your customers and prospects. This includes not only the storage and organization of customer data, but also the design of optimal business processes – tailored to a satisfactory customer experience.
In addition to customer relationships, you also use a CRM program – or in this case, more aptly, an xRM system (Any Relationship Management) – to manage any other business relationship, whether with suppliers, dealers, partners or even your employees (keyword B2E).
Track interactions over 360
In addition to contact details, they also store service requests and preferences of your customers. They record phone calls, e-mails, meetings and presentations and file notes, files, appointments, contracts, products and further planning directly in the electronic customer file. Today, 90 percent of communication takes place via e-mail clients. That’s why 100% email integration with the customer management system is hugely important.
This means that your employees can quickly access all the latest information and letter or e-mail templates, as well as forms, etc., at any time in order to advise your customers individually or provide them with relevant content via e-mail marketing, for example. Every user benefits from an easy, manageable workflow while your company’s customer base and profits grow.
This is an enormous relief in the area of operational customer relationship management.
Fluid processes and valuable insights
With practical overviews, helpful resubmissions and cross-departmental workflows, your sales department benefits immensely from the CRM system. He no longer misses opportunities thanks to the Follow-Up function. Extensive knowledge about your customers supports the perception of opportunities also in up- and cross-selling or in key account management. Thanks to CRM, sales management gains systematic insights into day-to-day business, optimizes the efficiency of processes, and keeps an eye on figures and targets, for example for forecasting and conversion rates.
In marketing, your employees recognize your potential customers precisely and address them unerringly. Both departments actively handle the CRM campaigns with phone and email campaigns via campaign management.
The quality of service also increases, thanks to faster response times and extensive background information on every customer inquiry, as well as access to know-how for customers as a self-service. Thanks to the ticket system and time recording, not only is organization easier, but the department manager also keeps an optimum eye on current issues and the efficiency of processes.
Department heads and top management benefit from the customer data in the system. Dashboards and reports support them in controlling the company.
What are its essential characteristics?
In addition to versatile functions, features of a CRM system are useful in supporting your company at various stages of the business process. Some properties serve as the basis for central and transparent communication within the company. Others provide targeted support for sales, marketing and service as well as their exchange.
Typical functions of a CRM system
- DSGVO compliant contact management
- Interdepartmental teamwork
- Higher productivity and efficiency
- Modern sales management
- Accurate sales forecasts and corporate management
- Reliable reporting functions
- Better sales metrics
- Higher satisfaction and customer loyalty
- Better marketing ROI
- Valuable suggestions for products and services
GDPR IN CRM
When it comes to data collection and processing, there is no way around the legal provisions of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) today. Compliance with all the specifications is not even trivial. Accordingly, it is a great advantage for you and your employees if your CRM system can already demonstrate the most important basic functions for compliance with the GDPR. This saves laborious training of individual employees and, not least, high fines for faulty data processing. Read more about what you need to consider in view of DSGVO in CRM and what the 100% DSGVO compliant GEDYS IntraWare CRM offers you.
CRM and email integration
One important integration is between CRM and email. In daily business, email has long since established itself as the most widely used medium for communication. Accordingly, you can probably easily imagine the advantages of having the email and CRM systems working together seamlessly. Get a 360° overview of the sender already in the e-mail program with all the data your CRM system has to offer. Or create a new contact in CRM directly from the email. With the email integration “BusinessMail ®” this is easily possible – fewer clicks and faster work.
And it does this for a wide range of the most popular email systems, as well as all IMAP mailboxes:
- CRM with Outlook
- CRM with HCL Notes
- CRM with HCL Verse
- CRM with IMAP mailboxes
CRM tip: Don’t forget data quality
The functionality of your CRM system is largely based on the processing of your business data. In order to achieve reliable and accurate results, not only the quality of the CRM processes but also that of the data must be right.
Read more about why data quality is so important and how to get it in our blog, “You Need More Data Quality in CRM!”
DQM CIRCLE

The CRM software comparison
How do you make the right choice?
When choosing a CRM, the most important thing is to consider what your business needs. This means that you should look at your processes, structures and business procedures and determine where functions of a software can be helpful and which functions you can do without.
Here, think about the important questions: Do we want to use an on-premise or cloud solution? And if so, as software-as-a-service? From there, it’s a lot easier to define your must-haves and thus include or exclude vendors.
Brief comparison of some advantages and disadvantages
| Cloud-based / SaaS | Server Client / On Premise | |
|---|---|---|
| Benefits | Quick setup | Internal data sovereignty |
| Hardly any investment at the beginning | Offline and online use | |
| High flexibility to users, modules, configuration, runtime etc. | Individual adaptation feasible = customizing | |
| Always current software version | ||
| Disadvantages | Online only = via browser | Internal IT necessary |
| Data sovereignty lies externally with the provider | IT staff or external service to operation and maintenance | |
| Initially high investment in software and hardware | ||
Valuable tips for comparison
Our blog article 9 Questions for CRM Comparison will help you ask yourself the right questions before you start vendor selection. Note: A good customer system integrates into your existing IT infrastructure and connects to your ERP system in the best possible way.
Checklist for your CRM selection
Use our checklist CRM requirements to compare the functions of different providers and define your own requirements for the right software in a specification sheet.

What are the current technical types of CRM?
Customer relationship management software is fundamentally based on a central CRM database that stores information and documents about your customers and prospects. These can then usually be accessed at any time, from any location and by any employee. Where the data is stored and how it is accessed makes some differences.
Cloud-based CRM (SaaS)
A cloud CRM system – i.e. a CRM as SaaS (Software as a Service) – is characterized in particular by its high flexibility and low effort. Software and databases operate in the cloud, offering such high performance and storage capacity with a stable Internet connection. Hardware, operating and infrastructure costs as well as maintenance expenses are all on the provider’s side and are transparently included in the rental price. Without any additional technology, all employees can access the system from any location via a simple browser. Practical licensing models make it easy to increase or decrease the number of users to be financed, which is a great advantage especially for growing companies. Modern hosting in Germany also ensures the necessary data security.
Server client = on-premises
In the on-premises model, the user purchases the CRM software and operates it under his own responsibility in the in-house or specially rented data center. The concern, but also the control of hardware, operation, infrastructure and maintenance work, therefore, all lie with the user himself, for which additional IT personnel are usually hired. What on-premises models lose in flexibility, they usually make up for in customization options. Accordingly, they are suitable for companies that have particularly individual requirements for their CRM software.
You can read more about the question of whether cloud CRM or on-premises in our blog article “Better Cloud or On-Prem?“.
What is a CRM app?
A CRM app for mobile devices is ideal for all companies that have employees in the field. They can access CRM data and functions from anywhere at any time without having to have a desktop with them. While a regular connection to the Internet is useful for keeping the data up to date, it can also be accessed offline – changes are then immediately synchronized the next time the Internet is connected. Dictation functions or route planners also ensure optimum effectiveness on the move.
Integrations & Interfaces
Integrations and interfaces enable CRM systems to access uniform data sets or transfer data from one system to another. This is of great importance when it comes to central and transparent corporate processes.
The most important link here is certainly the one with the ERP system. This involves very basic data on customers such as products purchased and payment transactions. But interfaces and integrations also pay off at other process points such as service organization, quotation preparation, sales control, route and tour planning or telephone connection for efficient working methods.
What does a CRM cost?
The cost of a CRM system depends heavily on the choice of technical basis and the degree of customization of the functions. From free offers with the usual basic functions and for small teams to variants with a high level of customization, you will find a wide range of options on the market, so there should be something for every budget.
SaaS CRM
The CRM system from the cloud brings decisive advantages and is suitable for companies that have fewer individual requirements for their CRM software and want to get started quickly. You save extensive investments in IT landscape and personnel because hosting can usually be rented directly. This makes CRM costs particularly clear and the service can be easily extended with maintenance services or additional modules if required.
For example, you can rent the GEDYS IntraWare Cloud CRM with all basic functions from just 59€ per month per user. As required, you can expand modules, configure individually, receive training or additional services such as maintenance and support.
Server client
Is an off-the-shelf CRM system not enough for you? The optimal solution for your business sometimes needs to be tailored. This may cost you a little more in case of doubt, but it pays off. Because customized CRM means optimal efficiency in your processes and saved time and nerves for your employees.
Whether as an in-house or web solution – at GEDYS IntraWare we welcome every challenge and create the perfect solutions for every business requirement in close cooperation with our customers. Depending on the special customizing of our software, you can get your individual CRM solution starting at 30.000€.
Introduction of a customer management system
Once the selection of a (cloud-based) CRM system has been made, a competent consultant is ideally at your side. Nevertheless, the process of software implementation hides some pitfalls. Read our blog article The 7 Phases of Implementing a CRM System to learn what to expect now and what to look out for.
Free e-books on the subject
- For more information, see our wiki page on CRM implementation.
- Or in our detailed e-book In 15 Stages to CRM – From CRM Idea to Implementation.
The right use of your customer loyalty system
Dos & Don’ts for and after CRM implementation
1. DON’T:
See Customer Relationship Management as software only
Remember that this is not just about integrating a software into your business, but much more still about implementing your customer strategy.
2. DO:
Involve employees
The implementation project stands and falls with your employees. Include input from your employees, make sure they are aware of the benefits of customer relationship management and receive the appropriate training to use the new software.
3. DO:
Evaluate customer system regularly
The tool lives and grows with your business. It is therefore important to review the system and strategy at regular intervals with regard to processes, users and technology, and to consider updates if necessary.
4. DON’T:
Expect ROI directly
The ROI of your CRM system will not occur overnight. This is a process that takes time. However, even before the introduction, think about which data you can use to determine and check the ROI (e.g. customer satisfaction). You will see that success will come.
5. DO:
Communication!!!
Maintain open communication with your employees and the CRM team. If difficulties or suggestions for improvement are not heard and discussed, the customer loyalty software cannot work optimally for your company and will not bring the successes you desire.
Examples of CRM systems in use
Please click on the logos to go to the reference stories.




The most important facts about CRM and CRM system at a glance
- CRM definition: Customer Relationship Management, or CRM for short, stands for the orientation of business processes to the customer. It includes a comprehensive view of all customer data, interactions and touchpoints. In addition to the CRM strategy, CRM software provides technical support in implementing these goals.
- CRM Suitability: The nature of the need for CRM systems varies across the size and focus of individual teams, industries, and company sizes. Moreover, CRM software can also be helpful for xRM and manage all conceivable business relationships besides customer relationships.
- CRM benefits: In addition to better business relationships, CRM promotes productivity, customer retention, business forecasting, sales and marketing activities, and service performance.
- CRM forms: Whether in-house, from the cloud or as a mobile app. Depending on the requirements of the individual company, different technical forms of CRM systems are suitable.
- CRM networking: It is absolutely essential to realize that linking the CRM system with the rest of the IT landscape via interfaces and integrations is absolutely conducive to the full impact of CRM – from ERP to e-mail integration.
- CRM selection: First, think carefully about what you need and use these basic criteria to search specifically for a suitable CRM provider.
- CRM implementation: Take a step-by-step approach to implementing your CRM system and ensure that all employees are on board and aware of the CRM benefits.